Body Mechanics and Exercise
Select a Skill:
- » Moving the Person Up in Bed
- » Positioning the Person in Bed
- » Transferring the Person to a Chair or Wheelchair
- » Moving the Person to a Stretcher
- » Transferring the Person Using a Mechanical Lift
- » Assisting with Range-of-Motion Exercises
- » Helping the Person Walk
Take the Review Test:

Purpose

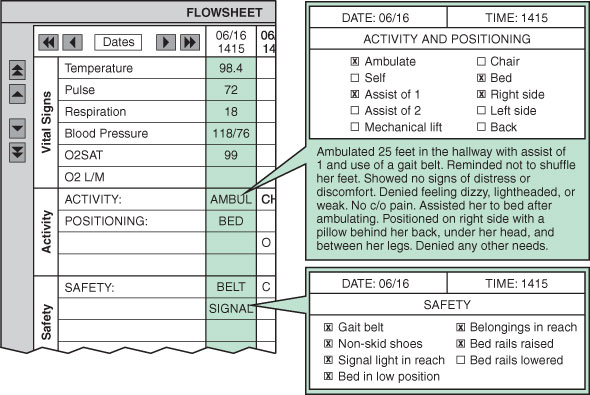
- Ambulation is the act of walking. Some people are weak and unsteady from bedrest, illness, surgery, or injury. They need help walking.
- After bedrest, activity increases slowly and in steps. First the person sits on the side of the bed (dangles). Sitting in a bedside chair follows. Next the person walks in the room and then in the hallway. This is true whether the patient walks with or without a gait belt or with a walking aid, such as a cane, a walker, crutches, or a brace.
- Follow the care plan when helping a person walk. Use a gait (transfer) belt if the person is weak or unsteady. The person also uses hand rails along the wall. Always check for orthostatic hypotension--weakness, dizziness, spots before the eyes, feeling faint.
- Walking aids support the body. The type ordered depends on the person’s condition, the support needed, and the disability. The physical therapist measures and teaches the person to use the device.
Equipment
Roll cursor over items to see labels. For the purposes of clearly depicting the equipment, a barrier is not shown in this photo. When providing care, a barrier should always be placed on the surface before placing the equipment.

Paper to protect bottom linens
Robe
Non-skid shoes
Gait (transfer) belt
Wheeled walker
Walker
Cane
Delegation
Follow delegation guidelines. Before helping the person walk, obtain this information from the nurse and care plan:
- How much help the person needs
- If the person uses a cane, a walker, crutches, or a brace
- Areas of weakness—right arm or leg, left arm or leg
- How far to walk
- What observations to report and record
- When to report observations
- What patient or resident concerns to report at once
Preparation

- Observe quality-of-life measures.
- Review the information under Delegation and Safety and Comfort.
- Collect the equipment.
- Practice hand hygiene.
- Identify the person. Check the ID bracelet against the assignment sheet. Also call the person by name.
- Provide for privacy.
Safety

- Practice safety measures to help prevent falls.
- Use a gait belt to help the person stand. Also use it during ambulation.
- Remind the person to walk normally.
- Encourage the person to stand erect with the head up and the back straight.
- Discourage shuffling, sliding, and walking on tip-toes.
- If crutches are used, check the tips, which must not be worn down, torn, or wet. Check crutches for flaws and tighten all bolts. Have the person wear street shoes and clothes that fit well. Keep crutches within the person’s reach.
- If a wheeled walker is used, move the wheels to the inside of the walker, if needed, to fit through narrow doorways. If the walker has a seat, never push the walker when the person is seated.
Comfort
The fear of falling affects mental comfort. Explain the purpose of the gait belt. Also explain how you will help the person if he or she starts to fall.
Procedure Video
Audio Description: OFFFollow-up Care
- Provide for comfort.
- Place the call light within reach.
- Raise or lower the bed rails. Follow the care plan.
- Return the robe and shoes to their proper place. If a walking device was used, put it near the person.
- Unscreen the person.
- Complete a safety check of the room.
- Practice hand hygiene.
Reporting/Recording
Report and record your observations, including:
- How well the person tolerated the activity
- Shuffling, sliding, limping, or walking on tip-toes
- Complaints of pain or discomfort
- Complaints of orthostatic hypotension—weakness, dizziness, spots before the eyes, feeling faint
- The distance walked
Review Questions
Select the best answer.
1. When preparing to help a person walk, which action should you take?
 Explain the procedure, apply a gait belt, and help the person stand.
Explain the procedure, apply a gait belt, and help the person stand. Assist the person with putting on a robe and socks.
Assist the person with putting on a robe and socks. Ask a co-worker to carry a urinary drainage bag, holding it at waist level.
Ask a co-worker to carry a urinary drainage bag, holding it at waist level. Place a gait belt around the person’s upper chest under the arms.
Place a gait belt around the person’s upper chest under the arms.
Select the best answer.
2. When helping a person walk, which safety measure should you follow?
 Use a gait belt to help the person stand and walk.
Use a gait belt to help the person stand and walk. Stand at the person’s stronger side while walking.
Stand at the person’s stronger side while walking. Stop walking and call the doctor if the person reports pain.
Stop walking and call the doctor if the person reports pain. Encourage the person to walk as quickly as possible.
Encourage the person to walk as quickly as possible.
Select the best answer.
3. How should the person walk?
Select the best answer.
4. If a person uses a wheeled walker, how should you assist with moving through a narrow door?
 Turn the walker and help the person move sideways through the door.
Turn the walker and help the person move sideways through the door. Move the wheels to the inside of the walker to fit through the door.
Move the wheels to the inside of the walker to fit through the door. Push the walker through the door with the person seated on it.
Push the walker through the door with the person seated on it. Remove the bulky wheels from the walker until it is through the door.
Remove the bulky wheels from the walker until it is through the door.
Select the best answer.
5. While helping a person walk, which complaint may indicate orthostatic hypotension?
You have completed the Review Questions for this skill. To take the Review again select the Start Over button. To proceed to another skill select from the dropdown menu. Select the Home or Back button to proceed to the next section.

