Measurements and Vital Signs
Select a Skill:
- » Measuring Weight and Height
- » Taking a Radial Pulse
- » Taking an Apical Pulse
- » Counting Respirations
- » Taking a Temperature with an Electronic Thermometer
- » Measuring Blood Pressure
- » Using a Pulse Oximeter
Take the Review Test:

Purpose

- The apical pulse is over the heart. The apex (apical) of the heart is at the tip of the heart, just below the left nipple. This pulse is taken with a stethoscope.
- A stethoscope is an instrument used to listen to the sounds produced by the heart, lungs, and other body organs. When using a stethoscope:
- Place ear-pieces in your ears. The bend of the tips points forward. Ear-pieces should fit snugly to block noise. They should not cause pain or discomfort.
- Tap the diaphragm gently. If you do not hear the tapping, turn the chest piece at the tubing. Gently tap again. Proceed if you hear the tapping. Check with the nurse if you do not.
- Place the diaphragm over the pulse site and hold it in place.
- Prevent noise. Do not let anything touch the tubing. Ask for silence.
- The pulse rate is the number of heartbeats or pulses felt or heard in 1 minute.
- The pulse rate is affected by many factors, including activity, drugs, and pain.
- The adult pulse rate is between 60 and 100 beats per minute. A rate of less than 60 or more than 100 is abnormal. Report abnormal pulses at once.
- The pulse rhythm should be regular. That is, pulses are felt in a pattern. The same interval occurs between beats. An irregular pulse occurs when the beats are not evenly spaced or beats are skipped.
- You will take radial and apical pulses. You must count, report, and record accurately.
- The apical pulse is on the left side of the chest slightly below the nipple. Use a stethoscope and count the pulse for 1 minute. The heartbeat normally sounds like lub-dub. Count each lub-dub as one beat.
- Apical pulses are taken on persons who:
- Have heart disease.
- Have irregular heart rhythms.
- Take drugs that affect the heart.
Equipment
Roll cursor over items to see labels. For the purposes of clearly depicting the equipment, a barrier is not shown in this photo. When providing care, a barrier should always be placed on the surface before placing the equipment.
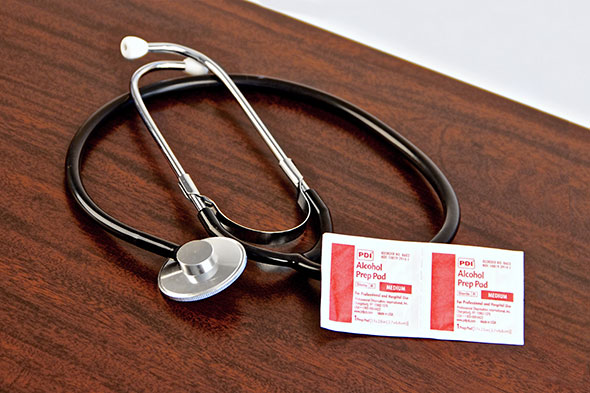
Stethoscope
Antiseptic wipes
Delegation
- Follow delegation guidelines. Before taking an apical pulse, obtain this information from the nurse and care plan:
- What pulse to take for each person—radial or apical
- When to take the pulse
- What other vital signs to measure
- How long to count the pulse—1 minute for an apical pulse
- If the nurse has concerns about certain patients or residents
- What observations to report and record
- When to report the pulse rate
- What patient or resident concerns to report at once
Preparation

- Observe quality-of-life measures.
- Review the information under Delegation and Safety and Comfort.
- Practice hand hygiene.
- Collect a stethoscope and antiseptic wipes.
- Identify the person. Check the ID bracelet against the assignment sheet. Also call the person by name.
- Provide for privacy.
Safety

- Stethoscopes are in contact with many persons and staff. You must prevent infection. Wipe the ear-pieces and diaphragm with antiseptic wipes before and after use.
Comfort
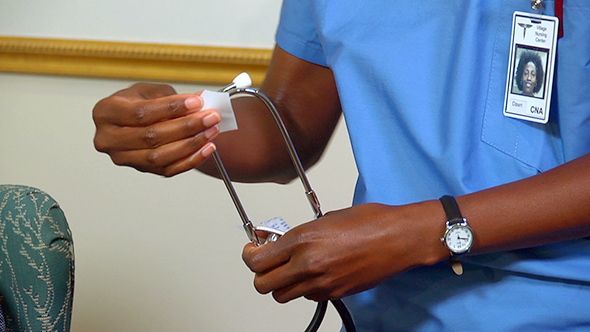
- Stethoscope diaphragms tend to be cold. Warm the diaphragm in your hand before applying it to the person. Cold diaphragms can startle the person.
Procedure Video
Audio Description: OFFFollow-up Care
- Provide for comfort.
- Place the call light within reach.
- Unscreen the person.
- Complete a safety check of the room.
- Clean the ear-pieces and diaphragm with the wipes.
- Return the stethoscope to its proper place.
- Practice hand hygiene.
Reporting/Recording
- Report and record your observations, including:
- The pulse site
- The pulse rate—report at once a pulse rate less than 60 (bradycardia) or more than 100 (tachycardia) beats per minute
- If the pulse is regular or irregular
- Pulse force—strong, full, bounding, weak, thready, or feeble
- Record the pulse rate with Ap for apical.
Review Questions
Select the best answer.
1. What is the normal apical pulse for a healthy adult?
 40 to 80 beats per minute
40 to 80 beats per minute 60 to 100 beats per minute
60 to 100 beats per minute 80 to 120 beats per minute
80 to 120 beats per minute 100 to 140 beats per minute
100 to 140 beats per minute
Select the best answer.
2. When is the apical site commonly used for taking a pulse?
 When the person has a respiratory problem
When the person has a respiratory problem When the person has an IV in his or her arm
When the person has an IV in his or her arm When the person has irregular heart rhythms
When the person has irregular heart rhythms When the person is a school-age child or teenager
When the person is a school-age child or teenager
Select the best answer.
3. In an adult, what term describes an apical pulse below 60 beats per minute?
Select the best answer.
4. Where is an apical pulse taken?
 On the side of the neck next to the jaw
On the side of the neck next to the jaw On the inside of the wrist below the thumb
On the inside of the wrist below the thumb On the inside of the arm at the bend of the elbow
On the inside of the arm at the bend of the elbow On the left side of the chest slightly below the nipple
On the left side of the chest slightly below the nipple
Select the best answer.
5. If the apical pulse is irregular, how should you determine the pulse rate?
 Count for 15 seconds and multiply by 4
Count for 15 seconds and multiply by 4 Count for 30 seconds and multiply by 2
Count for 30 seconds and multiply by 2 Count for 1 full minute
Count for 1 full minute Count for 2 full minutes
Count for 2 full minutes
You have completed the Review Questions for this skill. To take the Review again select the Start Over button. To proceed to another skill select from the dropdown menu. Select the Home or Back button to proceed to the next section.

